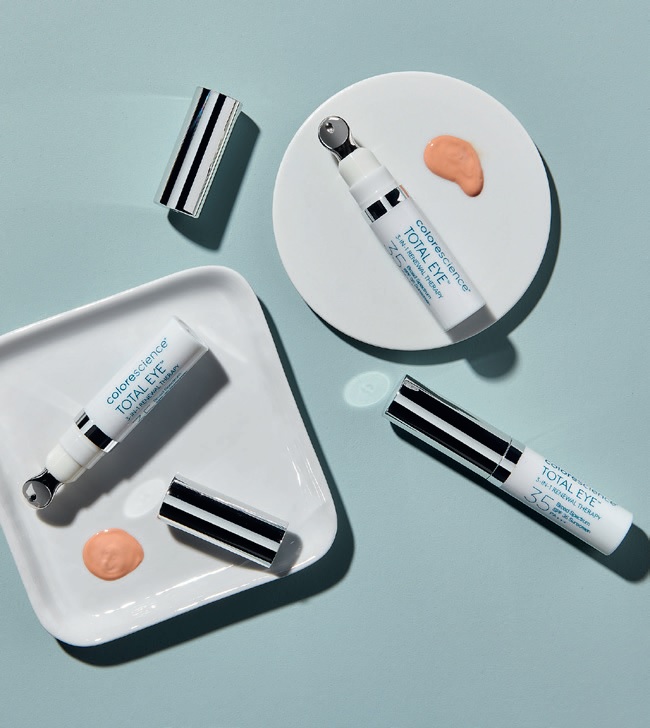
HEV (blue light) is a high-frequency, high-energy light with a wavelength range between 400 nm and 760 nm. HEV exposure has increased dramatically with the expanding use of consumer electronics like smartphones, which reach a peak emission in the 400-490 nm range. A new study from Colorescience, assesses the effects of HEV exposure and the efficacy of iron oxides in attenuating blue light rays when included in skincare formulations.
The effect of blue light on skin
Clinically, the damage of HEV exposure is similar to the damage caused by long wavelength UVA rays as they both rely on free radical formation in contrast with UVB radiation which exerts its effects through DNA damage. Analysis of tissue cultures exposed to HEV light revealed impaired fibroblast growth, altered cell distribution, and decreased type I procollagen production.
Furthermore, when human subjects with Fitzpatrick skin types II and IV-VI were irradiated with UVA1 (340-400nm) and HEV light (400-700nm), both wavelength ranges caused increased pigmentation; however, the pigmentation induced by HEV light was darker and more sustained than that produced by UVA. When compared with UVB, exposing subjects with skin types III and IV to blue light resulted in significantly more marked hyperpigmentation that lasted up to three months.

Protecting against HEV
The daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential to the treatment and prevention of hyperpigmentation. However, UV-absorbing chemical ingredients such as oxybenzone, avobenzone, and octocrylene have limited to no data demonstrating their ability to attenuate blue light. Zinc and titanium dioxide can attenuate wavelengths in the mid-400 nm range but provide limited protection against visible and near-infrared radiation.
In Colorescience’s recent study, red (Fe2O3), yellow (Fe(OH)3/FeOOH) and black (Fe3O4) iron oxides have shown to provide and effective shield against HEV. Each iron oxide has a different light attenuation profile that allows them to maximally attenuate HEV in various nanometre segments of the blue light range. Products formulated with zinc oxide, titanium dioxide and iron oxides demonstrated 71.9% to 85.6% attenuation across the tested wavelengths of 415 to 465 nm. The attenuation of HEV 400 nm to 490 nm light was measured in vitro using a diffuse transmittance spectroscopy.

Iron oxides are included in Colorescience’s All Calm Clinical Redness Corrector SPF 50, Even Up Clinical Pigment Perfector SPF 50, and Total Eye 3-in-1 Renewal Therapy SPF 35 formulations alongside zinc and titanium dioxide to provide a safe, effective, and environmentally friendly protection against HEV.
Colorescience is available at Wigmore Medical, call Customer Services on 020 7491 0150 for more information.

 Added to basket
Added to basket

 Unapplied Changes
Unapplied Changes